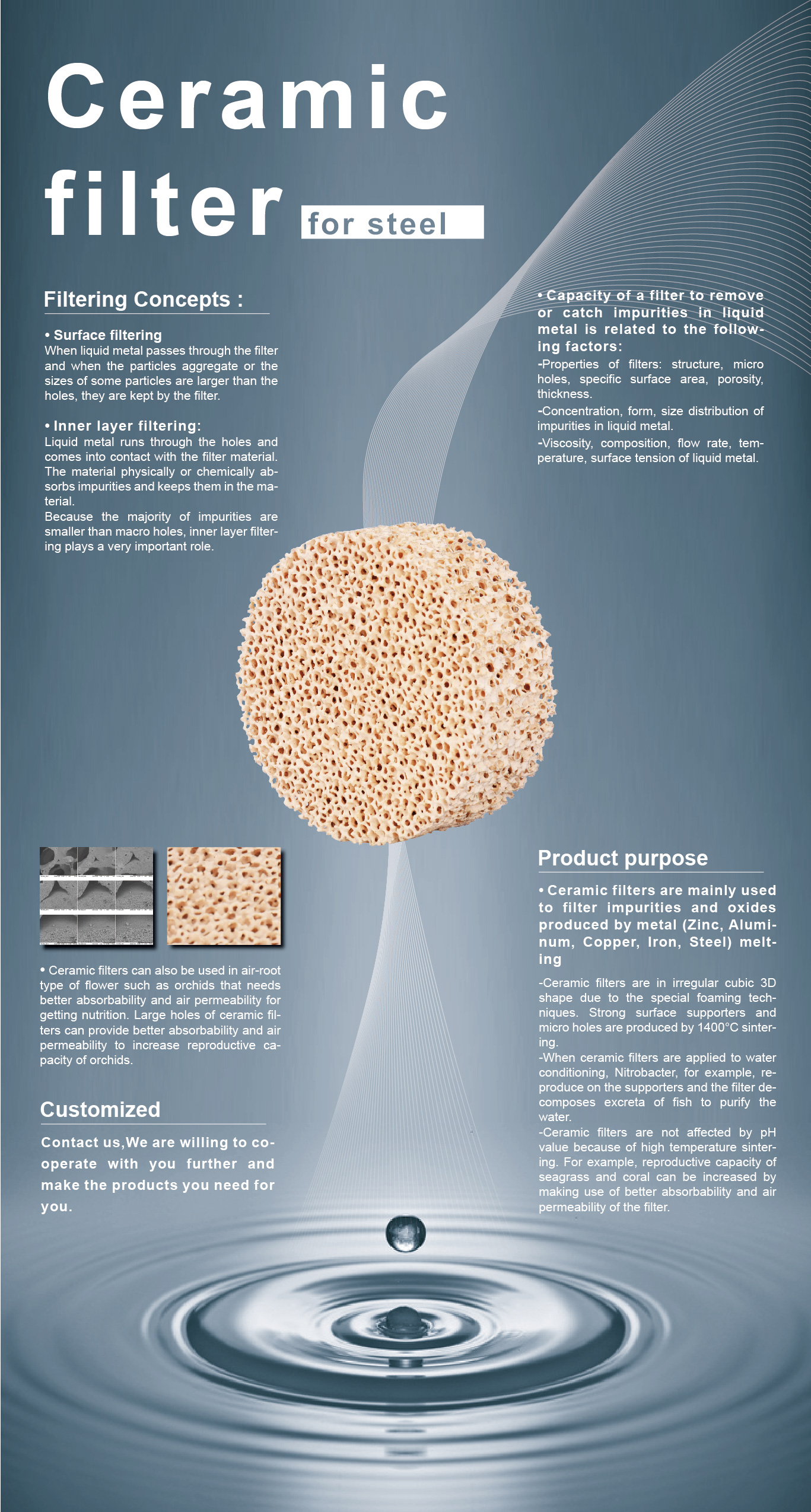
Ceramic Filter Types: Zirconia (Steel Casting)
Filtering Concepts of Ceramic Filters:
Surface filtering:
When liquid metal passes through the filter and when the particles aggregate or the sizes of some particles are larger than the holes, they are kept by the filter.
Inner layer filtering:
Liquid metal runs through the holes and comes into contact with the filter material. The material physically or chemically absorbs impurities and keeps them in the material.
Because the majority of impurities are smaller than macro holes, inner layer filtering plays a very important role.
Capacity of a filter to remove or catch impurities in liquid metal is related to the following factors:
◎Properties of filters: structure, micro holes, specific surface area, porosity, thickness.
◎Concentration, form, size distribution of impurities in liquid metal.
◎Viscosity, composition, flow rate, temperature, surface tension of liquid metal.
Ceramic filters are mainly used to filter impurities and oxides produced by metal (Zinc, Aluminum, Copper, Iron, Steel) melting.
Ceramic filters are in irregular cubic 3D shape due to the special foaming techniques. Strong surface supporters and micro holes are produced by 1400°C sintering.
When ceramic filters are applied to water conditioning, Nitrobacter, for example, reproduce on the supporters and the filter decomposes excreta of fish to purify the water.
Ceramic filters are not affected by pH value because of high temperature sintering. For example, reproductive capacity of seagrass and coral can be increased by making use of better absorbability and air permeability of the filter.
Ceramic filters can also be used in air-root type of flower such as orchids that needs better absorbability and air permeability for getting nutrition. Large holes of ceramic filters can provide better absorbability and air permeability to increase reproductive capacity of orchids.